How Solar Panels Work: A Guide to Turning Solar Energy into Electricity
As more people look to make sustainable choices for both the environment and their wallets, solar energy is becoming increasingly popular. But how do solar panels actually work? Let’s take a closer look at this technology that converts the sun’s energy into electricity and how solar panel systems are structured.
Solar Energy and Solar Power
Before diving into the details of solar panels, let’s clarify an important distinction:
- Solar energy refers to all the energy present in sunlight.
- Solar power is the electricity generated from solar energy.
Two Main Ways to Harness Solar Energy
There are two primary methods for utilizing the sun’s energy:
- Solar collectors – These are used to heat water for heating and domestic use.
- Solar panels – These directly convert solar energy into electricity, which is our focus in this article.
How is a Solar Panel System Structured?
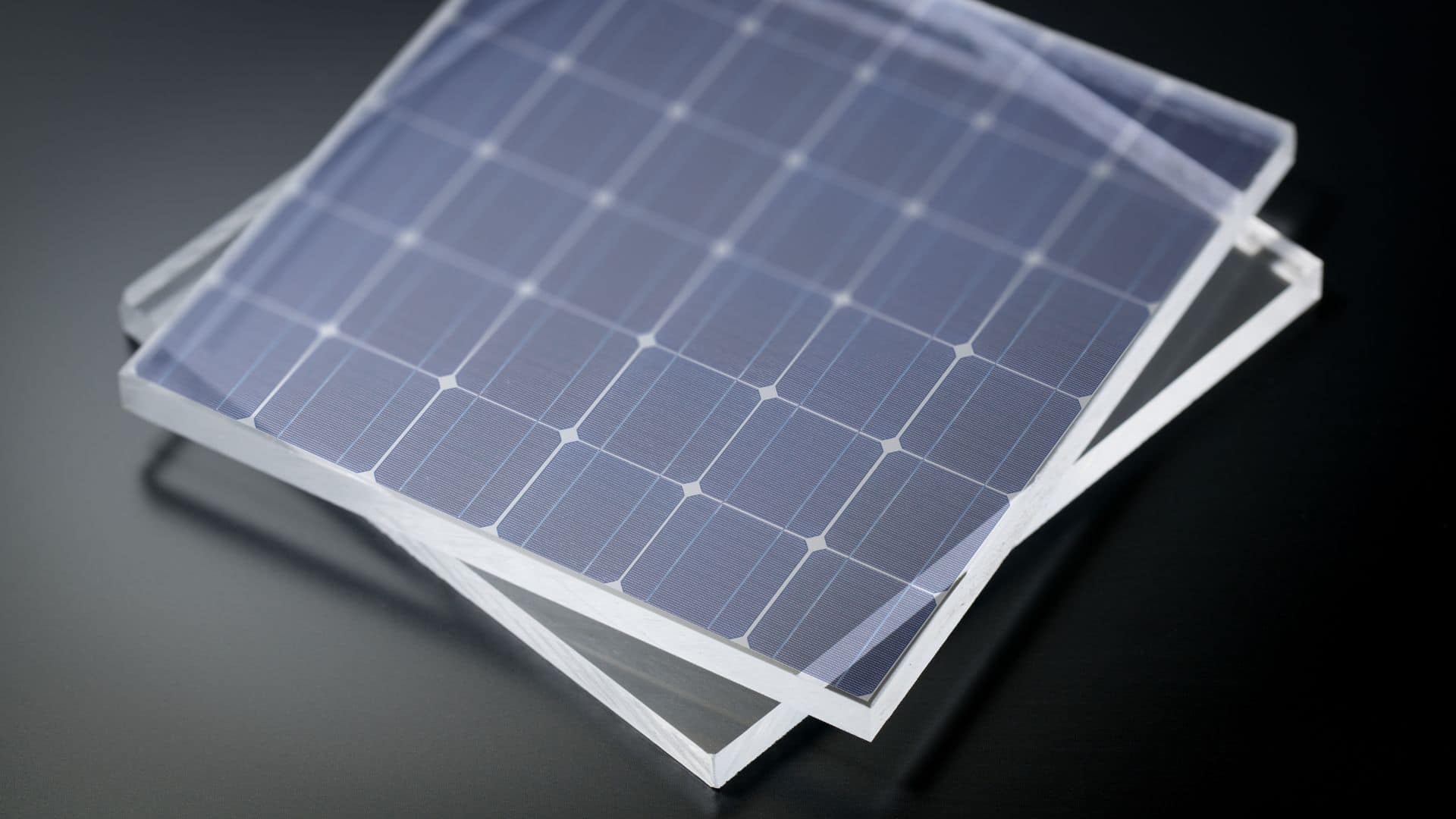
A solar panel system consists of multiple panels, each made up of smaller components. Here is a simplified description of the six basic parts of a solar panel:
- Aluminium frame – The outer frame holds the panel together and protects the internal components from damage. It also makes the panels easier to transport and install.
- Tempered glass – The glass protects the solar cells from weather and other damage. It allows more light to pass through than regular window glass and often has an anti-reflective coating to minimize light reflection and increase efficiency.
- Solar cells – The actual solar cells are embedded between two layers of protective lamination material. These cells are often connected in series, and a panel usually contain 60 or 72 cells depending on its size.
- Back sheet – The back of the panel protects the solar cells. The most common type is opaque, but some models have glass backs that allow light to pass through both sides, which can increase efficiency but also raise costs.
- Junction box – This is where the panels are connected to form a complete solar panel system.
Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline Solar Cells
There are two main types of solar cells: monocrystalline and polycrystalline. Both are made from silicon but have different atomic structures:
- Monocrystalline solar cells: These have a more orderly structure where the atoms are symmetrically arranged in rows, making them more efficient at capturing solar energy. They offer higher efficiency but are also more expensive.
- Polycrystalline solar cells: These have a less organized atomic structure, making them slightly less efficient but more affordable.
Nowadays, monocrystalline panels are the most commonly sold, as they provide better efficiency and performance.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
When sunlight hits the solar cells, they absorb some of the energy. This causes electrons in the solar cells to move, generating an electric current. This current can then be used as electricity.
Mounting Solar Panels
There are several ways to mount solar panels on a roof, depending on the roof’s slope:
- Tilted systems: On low-slope roofs, panels are mounted on structures, usually at an angle between 10–15 degrees.
- Roof pitch installation: If the roof has a slope greater than 5-6 degrees, the panels are typically installed to follow the roof’s natural inclination.
The Most Common Installations:
- South-facing system: This setup generates the most electricity, especially during the hours when the sun is highest in the sky. However, to prevent the panels from shading each other, more space between rows is required, which demands more roof area.
- East-west system: This setup generates slightly less electricity per panel but a higher total production because more panels can fit in the same area. East-west installations produce energy more evenly throughout the day, which can be advantageous depending on your electricity consumption.
- Facade installations: These produce about 70% of the energy compared to roof installations and have a higher risk of shading and dirt buildup. Facade installations should be avoided if possible.
Other Equipment: The Inverter
Another essential component of a solar panel system is the inverter. Solar panels generate direct current (DC), but most appliances and the power grid use alternating current (AC). The inverter converts the generated DC electricity into AC electricity that can be used in your property or fed into the grid.
Conclusion
Solar panels are an amazing technology that converts the sun’s energy into electricity and contributes to a sustainable future. By understanding how solar panels are built and how installation works, you can optimize the efficiency of your solar panel system. Whether you have a well-angled roof or limited space, there are solutions to fit your needs. Solar energy is not only beneficial for the environment but can also be a long-term financial investment.
With BIM Energy, you can model solar panels to see how they interact with your specific property. The software calculates electricity usage at a minute level, providing a highly accurate picture of actual savings.